Anatomy, Hair Follicle StatPearls NCBI Bookshelf
Table Of Content
Each human follicle follows this cycle independently of others, so the total amount of hair remains constant; some animals’ hair follicles have synchronous cycles, causing periodic shedding, or molts. Anagen growth is the active phase in which the hair follicle takes on its onion-like shape and works to produce the hair fiber. The anagen phase can be further broken down into proanagen and metanagen phases. Proanagen sees the follicle proliferating hair progenitor cells and begins the differentiation process. The new hair shaft appears on the skin's surface to mark the metanagen phase. Hair that is darker, thicker, and more visible to the human eye is called terminal hair.
How do I strengthen my hair follicles?
The corresponding peak positions and distributions are shown in the figure. The 90 Å peak has been reported early in the literature as the distance between intermediate filaments in human hair. Also here, the standard deviations of 90 ± 2 Å, 47 ± 2 Å, 27 ± 1 Å, as shown in the figure, are small, indicating that the organization of the intermediate filaments on the nanoscale varies very little between different individuals. 1 in the equatorial plane (q‖) (A), and along the axis of the hairs (qz) (C), respectively, for all subjects. The two signals present in all individuals in the equatorial plane (q‖) correspond to the distance between two coiled coils of 9.5 Å and between two lipid tails in the cell membrane cortex of 4.3 Å.
Hair Follicle
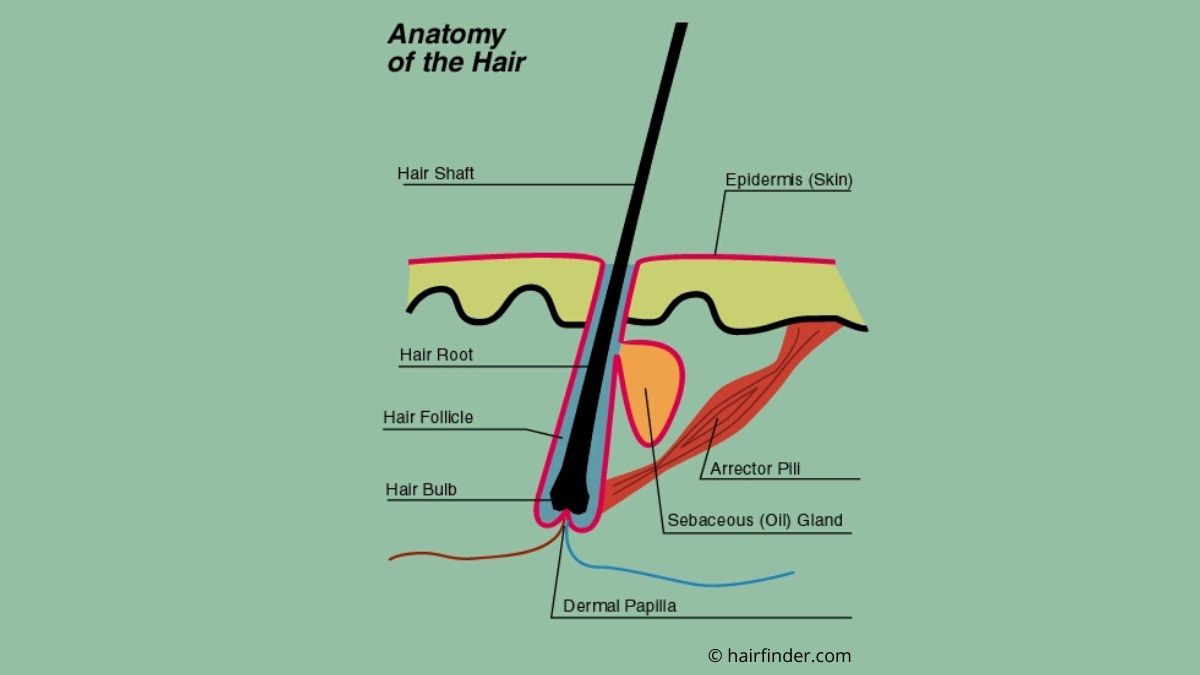
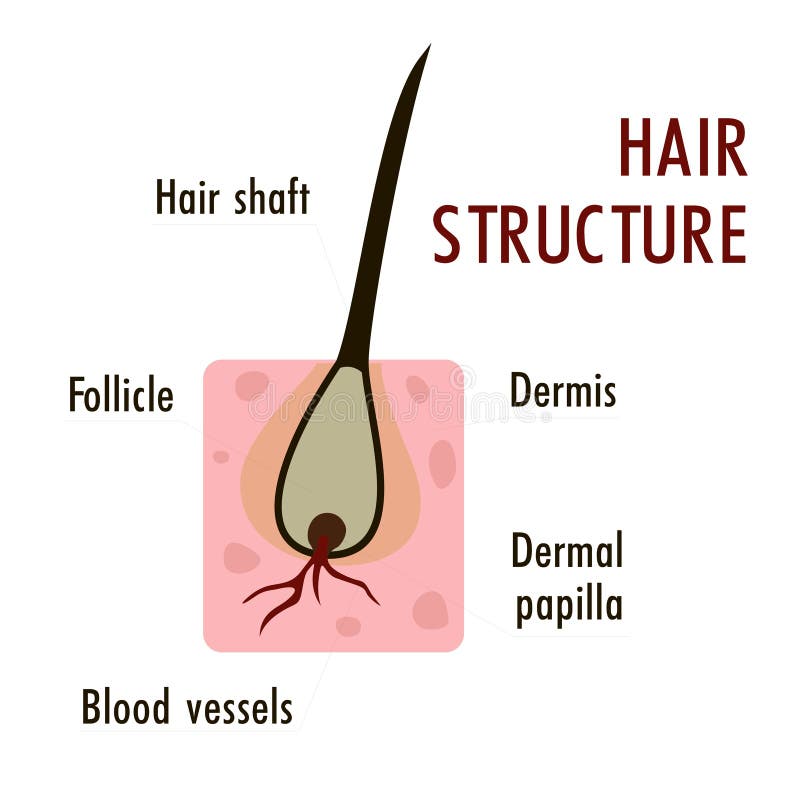
Finally, the inferior segment of the hair follicle extends from the bulge to the base of the follicle. This segment includes the bulb, which contains the follicular matrix surrounding the sides and top of the dermal papilla. The papilla interacts with the matrix, which has the highest mitotic rate of any organ.
General structural features from the X-ray experiments
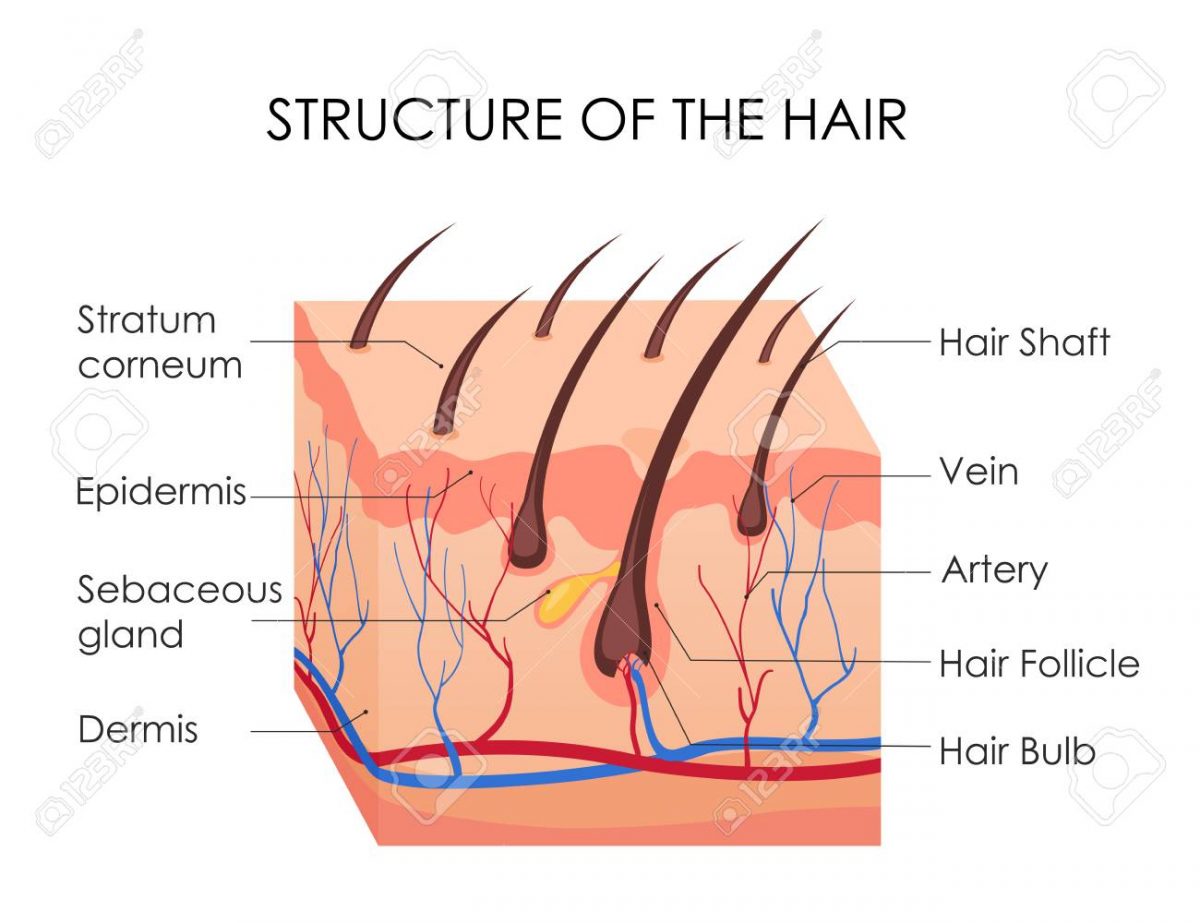
The hair bulb also contains cells called melanocytes that produce various kinds of melanin pigments. Their varying combinations are what help to produce the different natural hair colors people have. The shock of the event triggers the change in the hair growth cycle. It’s possible that a damaged follicle will stop producing hair. Certain conditions, such as alopecia, can cause follicles to stop producing hair altogether. Whether it is straight or curly will depend on the cross-sectional shape of hair.
In order to quantitatively determine the position of the corresponding scattering features, the 2-dimensional data for all 12 individuals were integrated in the equatorial plane (q‖-axis) of the hair fibres, and along the hair fibres (qz-axis). In the direction along the hair fibre axis (qz), there are two major peaks that were consistent among all subjects, one narrow peak around 5.0 Å and one broader peak around 4.3 Å. Some features were common in all specimens and assigned to certain molecular components, as explained in the next section. The hair samples gathered were cut into strands around 3 cm long. Care was taken to not stretch or deform the hair strands during this process. For each subject, around 10 strands were taped onto a flexible cardboard apparatus as shown in Fig.
Grey's Anatomy
The top of the cylinder is an open hole, which is where your hair grows out. Your follicle is similar to a sock; your hair is your foot that goes into your sock. The follicle is the primary structure from which hair can grow. The histological arrangement of the follicle is divided into outer and inner root sheaths.
This research was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), the National Research Council Canada (NRC), the Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI) and the Ontario Ministry of Economic Development and Innovation. MCR is the recipient of an Early Researcher Award of the Province of Ontario. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The specimen of most individuals showed 3 distinct reflections at ∼90 Å, 46.5 Å and 27 Å, related to the properties of intermediate keratin filaments (B). Integration of the 2-dimensional data was performed using Matlab, MathWorks. By adding up the peak intensities along the qz and the q‖ directions, 1-dimensional data along each of the two directions were produced.
Gray (hair's) anatomy discovered - Star Tribune
Gray (hair's) anatomy discovered.
Posted: Fri, 04 Mar 2016 08:00:00 GMT [source]
How It Gets Its Shape
The blade is brought close to the skin and stroked over the hair in the desired area to cut the terminal hairs and leave the skin feeling smooth. Depending upon the rate of growth, one can begin to feel the hair growing back within hours of shaving. This is especially evident in men who develop a five o'clock shadow after having shaved their faces. Stubble typically appears to grow back thicker because the shaved hairs are blunted instead of tapered off at the end, although the hair never actually grows back thicker. This melanin is stored in hair follicle cells, which then determine the color of the hair.
'Grey's Anatomy' star Camilla Luddington on Jo's season 18 journey - Entertainment Weekly News
'Grey's Anatomy' star Camilla Luddington on Jo's season 18 journey.
Posted: Wed, 27 Oct 2021 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Structure
On adult whales, elephants, sirenians, and rhinoceroses body hair is limited to scattered bristles. In most other mammals the hair is abundant enough to form a thick coat, while humans are among the most hairless of all mammals. Nerve supply to the hair follicles is similar to that of the surrounding network of dermal nerves in that it is composed of both sensory afferents and autonomic sympathetic nerves. Sensory information from hair stimulation enhances tactile ability. Autonomic nervous innervation primarily provides control of the arrector pili muscle.
The dermal papilla consists of an egg-shaped accumulation of mesenchymal cells surrounded by ground substance that is rich in acid mucopolysaccharides (AMPs). The papilla protrudes into the hair bulb and is responsible for instigating and directing hair growth. The histologic features of the hair follicle change continuously and considerably during the hair growth cycle, thereby making follicular anatomy an even more complex entity. A proliferation of fine lanugo hairs past the neonatal period can be a symptom of malnutrition and aid in diagnosing anorexia nervosa. Hair transplantation has become a therapeutic option for those who fail to have hair growth with medication.
These include the face, ears, head, eyebrows, legs, and armpits, as well as the pubic region. The highly visible differences between male and female body and facial hair are a notable secondary sex characteristic. Jablonski's assertions[52] suggest that the adjective "woolly" in reference to Afro-hair is a misnomer in connoting the high heat insulation derivable from the true wool of sheep. Further, wet Afro-hair does not stick to the neck and scalp unless totally drenched and instead tends to retain its basic springy puffiness because it less easily responds to moisture and sweat than straight hair does.
If you have any concerns about your hair growth, talk to a dermatologist. A 2017 article found a new method of reactivating dead or damaged hair follicles. However, this treatment hasn’t yet been tested on humans and it hasn’t been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Hair follicles aren’t just responsible for how much your hair grows, they also influence what your hair looks like. Circular follicles produce straight hair while oval follicles produce curlier hair.
During the hair cycle phases, there are some alterations in the density of perifollicular vascularization due to the upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression [1]. The hair follicle serves as a reservoir for epithelial and melanocyte stem cells and it is capable of being one of the few immune privileged sites of human body. Hair follicle development is related to the interactions between epithelial and mesenchymal cells. Many genes play substantial role in this interaction and also in hair follicle cycling [3–5].
1 between about 1.34 Å-1 and 1.63 Å-1, which are observed in some hair samples, agree with structural features reported in lipid membranes of different composition. Unsaturated lipids were reported to order in a structure with slightly larger nearest neighbour tail distances, leading to an acyl-chain correlation peak at ∼1.3 Å-1, as reported for DOPC and POPC (Mills et al., 2009), for instance. Lipids, such as Dimyristoylphosphatidylethanolamine (DMPE) and the charged DMPS (Dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoserine) with smaller head groups were reported to order in more densely packed structures (Rappolt & Rapp, 1996).
Different follicles go through different phases of the cycle at the same time. Some follicles are in the growth phase while others might be in the resting phase. Some of your hairs might be growing, while others are falling out. According to a 2015 article, recent research has suggested that hair follicles aren’t just “resting”’ during the telogen phase.
Comments
Post a Comment